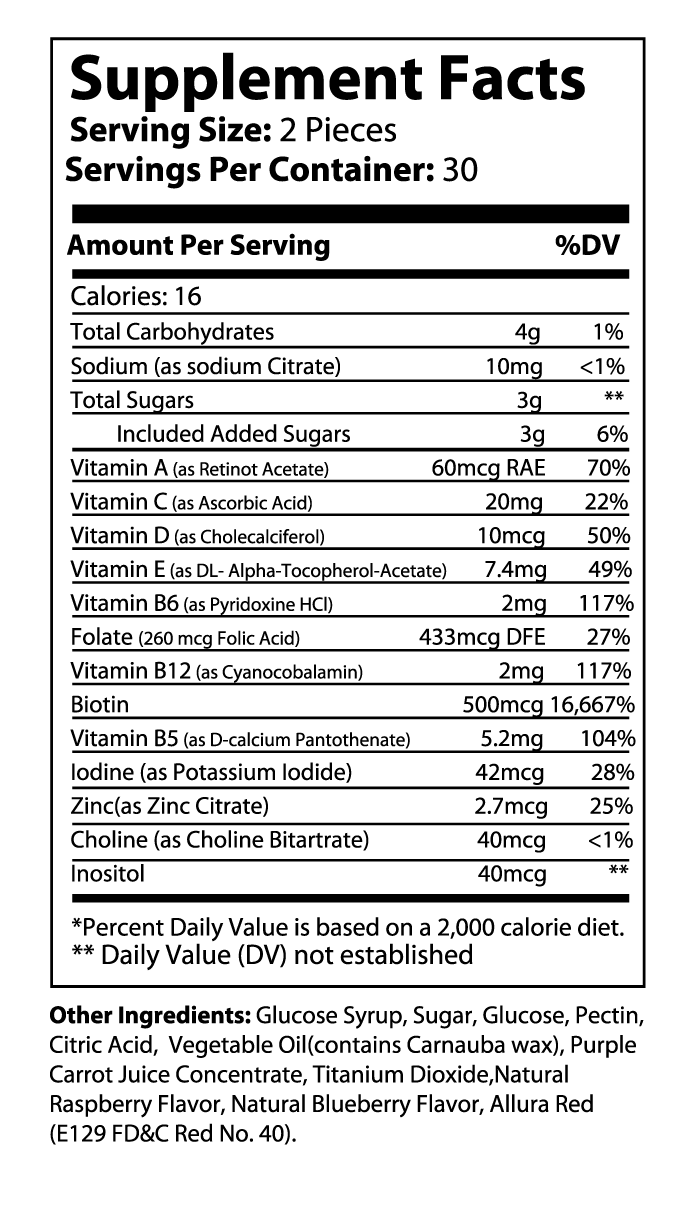
| Formula Ingredient Deck |
Benefits Of Each Ingredient |
| Vitamin A |
- Supports vision health, skin health, and immune health and increases antioxidant support (182, 183).
- Supports antioxidant function via decreased inflammatory cytokines (inflammation), decreased reactive oxygen species, and increased L-glutathione production (master antioxidant).
- Supports visual health via increased amounts of plasma vitamin A in macular (eye) tissues.
|
| Vitamin C |
- Supports immune, cardiovascular, skin, cognitive, fat-burning, and digestive health (97, 98).
- Supports immune health via increased oxidant, free radical scavenging, and fueling neutrophilic (immune cell) activity in chemotaxis, phagocytosis, and microbial killing (97,98).
- Supports fat burning by increasing carnitine biosynthesis (molecule required for mitochondrial fatty acid oxidation) (97,98).
- Supports accelerate bone healing after a fracture, increases type I collagen synthesis, and reduces oxidative stress (inflammation) (98).
|
| Vitamin D |
- Supports exercise performance, immune health, muscle growth, optimal bone health, hormonal health, immune function, increased sexual health, cardiovascular health, glucose tolerance, strength, and positive mood (77,78,79).
- Supports hormonal health via high amounts of vitamin D receptor (VDR) activity in hormone-based negative feedback loop reactions (77,78).
- Supports cardiovascular health via improved absorption of calcium, reduced atherosclerotic activity, stimulating cardiomyocytes, and improved vascular health (77,78).
- Supports exercise performance via reduced exercise-associated inflammation and muscle damage (77,78).
- Supports sexual health via increased activity of Vitamin D receptor activity of testosterone production (79).
- Supports immune function via decreases of inflammatory cytokines and aiding immune cells (77,78).
- Supports joint health via regulating calcium and phosphorus and bone remodeling along with other calcium-regulating actions (77,78).
|
| Vitamin E |
- Supports immune function, cognitive health, cardiovascular health, and bone health (204,205,206,207,208)
- Supports immune health via neutralizing free radicals and reactive oxygen species and increases T lymphocyte-mediated immune function (204).
- Supports cardiovascular health via reduced cholesterol (204).
- Supports cognitive function via reduced oxidative stress, inflammation, and DNA damage of neuronal tissues (208).
|
| Vitamin B6 |
- Serves as a cofactor in more than 150 enzymatic reactions associated in blood sugar regulation, immunity, cardiovascular function, neuronal health, metabolic, and digestive health (38, 40).
- Reduces plasma glucose (blood sugar levels) via by inhibiting the activity of small-intestinal α-glucosidases (enzymes associated with glucose metabolism) (39).
- Functions as an antioxidant by counteracting the formation of reactive oxygen species (inflammatory markers) and advanced glycation end-products (38,40).
- May support blood sugar regulation in women with gestational diabetes (40).
- Cofactor for enzymes involved in DNA metabolism (40).
|
| Vitamin B12 |
- Supports proper DNA synthesis, folate cycle function, energy production, cognitive function, and immune health (51,53).
- Aids as an antioxidant via direct scavenging of reactive oxygen species (inflammation), preserving l-glutathione levels (master antioxidant), and reducing oxidative stress (51).
- May prevent vitamin b-12 deficiency diseases such as anemia, neurodegenerative disease, cardiovascular disease, and osteoporosis (53).
|
| Folic Acid |
- May support proper cell growth and DNA synthesis (65).
|
| Vitamin B5 |
- Supports energy production, cell growth, cell repair, cognitive function, increased hippocampal volume (memory), and optimized bioenergetics (burning of carbohydrates, fat, and protein) (96).
|
| Biotin |
- Supports the conversion of food into cellular energy, hair health, skin health, and cognitive function (213,214).
- Enhances glucose breakdown into skeletal muscle tissue (213,214).
|
| Zinc |
- Supports immune function, skin health, cognitive function, and vision (172,173).
- Supports stimulation of the innate and adaptive immune system (172,173).
- Supports the activation of lymphocytes and activation of innate and T cell-mediated immunity (172,173).
- Supports cognitive function by modulation of neuronal signaling in areas of the brain associated with memory and learning (hippocampus) (172,173).
|
| Iodine/Kelp |
- High bioavailable source of iodine and polyphenols (32).
- May support healthy thyroid levels in individuals with impaired thyroid function (32).
|
| Inositol |
- Supports liver detoxification, combats metabolic syndrome, and aids as an antioxidant (221).
- Combats metabolic syndrome via reduced levels of triglycerides, total- and LDL-cholesterol (221).
- Supports antioxidant function via reduced levels of reactive oxygen species and inflammatory markers (interleukin 6) (222).
|
| Choline |
- Essential for cell membrane integrity, cell messaging, fat metabolism, DNA synthesis, immune support, and nervous system function (62,63).
- Serves as a methyl donor and as a precursor for the production of cell membranes (62).
- Precursor for acetylcholine (neurotransmitter) which activates receptors in the central nervous system mediated immune responses (α7nAchR) (64).
- Lifelong choline supplementation may combat neurodegenerative diseases by reducing amyloid-β plaque load (plaques of degrading neurons) (62).
- Reduces the concentration of total homocysteine (inflammation marker) in individuals with low levels of folate and other B vitamins (B₂, B₆, and B₁₂) (62).
|